Table of Contents
India’s power deficit stems from reduced hydroelectricity due to irregular rainfall and delayed coal-fired stations, crucial as coal powers 70% of its energy. Find out more reasons and strategies!
India’s electricity sector is under immense pressure to meet the power demands of a fast-growing population and an accelerating economy. This silent crisis, if not dealt with properly, will certainly upset India’s progress. That would involve interrupting the rhythm of progress in this country.
Currently, India’s electricity supply is a riddle where pieces are scattered across areas such as coal shortages, ageing infrastructure and population growth. The overheating electricity challenge must be addressed urgently – it is about national security, economic stability and environmental responsibility.
The article discusses the issue of electric power supply inadequacy in India and explores novel approaches to buttress energy infrastructure in the country to facilitate a smooth transition to sustainable renewable energy solutions that are both scalable and feasible over time.
Understanding the sustainable energy overheating problem
Overheating is not just a metaphor in the electricity supply sector; it is a reality. It implies that the electricity demand continues to outpace supply persistently, leading to pressure on power generation systems. The outcome of this is that power plants may be compelled to operate beyond their capacity, which results in equipment failure and widespread blackouts.
The latest Electricity 2024 Report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that India’s electricity demand will overtake China’s and have the fastest growth rate among all nations by 2026.India’s average annual growth rate of electricity demand is estimated at 6.5% between 2024-2026. This means that through such substantial expansion, India’s incremental electricity requirement during the next three years would almost equal the total consumption of the UK.
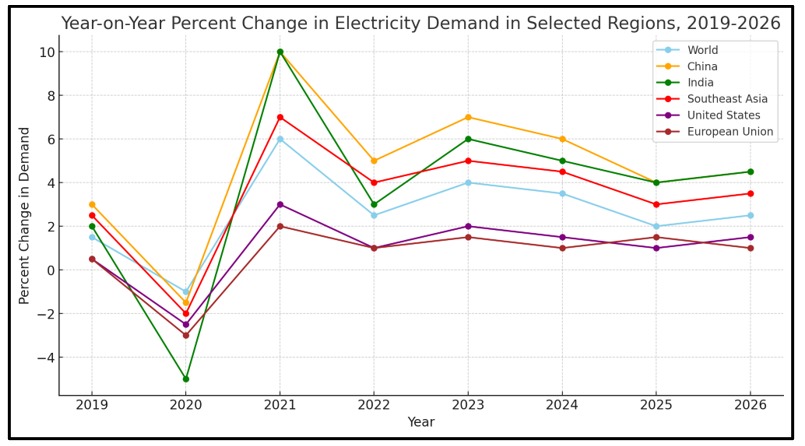
Source: IEA
There are various reasons why India suffers from power deficits. It can be attributed to a significant drop in hydroelectricity output due to erratic rainfall and delays in commissioning coal-fired power stations with 3.6 GW capacities. These were scheduled for completion by March but experienced delays hence contributing to an expected energy deficit. That is because about 70% of India’s total energy needs depend on coal.
The current state of renewable energy in India
There has been an impressive advance in India’s renewable energy sector, particularly in solar power which took the lead in February 2024. In terms of the share of the total nation’s renewable production, solar energy made up 57.9% and possessed an installed capacity of 75.575 GW.
Also, wind energy contributed a proportion of 27.27%. These sources together have brought India’s renewable capacity to 136.57 GW (excluding hydropower), indicating its dedication to alternative sources of clean energy and a greener tomorrow.
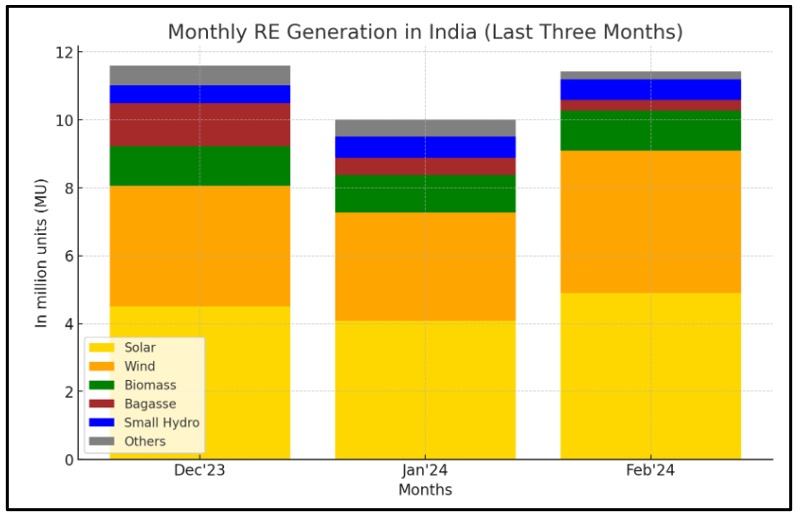
Source: Solar Quarter
The country is heavily investing in advanced energy solutions such as clean hydrogen, energy storage and carbon capture for which over $35 billion per annum should be spent by 2030. It has already gone beyond its renewable energy targets for 2030 and it is being helped into the transition through policy support and incentives.
India must however address the problem of expanding its renewable energy infrastructure and meet increasing demand while maintaining a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability.
Strategies to address electricity supply shortages
- Enhance traditional power plants:
- Upgrade equipment for better efficiency.
- Optimize fuel usage.
- Implement advanced technologies for increased output.
- Reduce transmission and distribution losses:
- Modernize grid infrastructure.
- Upgrade transmission lines.
- Deploy smart grid technologies.
- Demand-side management:
- Implement strategies to reduce peak-hour energy consumption.
- Promote energy-efficient appliances.
- Encourage energy-saving building designs and consumer behavior changes.
- Accelerate renewable energy transition:
- Improve grid integration of renewables.
- Increase renewable energy capacity to meet demand sustainably.
Boosting renewable energy to mitigate overheating
India has increased renewable energy to counter climate change and subside global warming. It was evident through the Union Budget 2024-25, which allocated ₹10,000 crore for grid-based solar power schemes, a significant increase from the previous year. Moreover, wind power alone got ₹930 crore, meaning diversified renewable sources are still being invested.

The government’s production-linked incentive schemes have attracted industry attention, resulting in a boom in green projects across the country. These incentives, viability gap funding (VGF), and tax credits have made such investments more attractive.
Furthermore, the government has initiated waivers on transmission, wheeling, and banking charges to lower the cost premium of advanced solutions and encourage adoption. It is likely to fast-track the deployment of renewable energy infrastructure and reduce reliance on conventional power sources.
Also worth noting are India’s strides in renewable energy technology. It has gone beyond its 2030 renewable energy goals ahead of time, showing how targeted policies, together with incentives, can work effectively. An example is the rooftop solarization scheme, which targets ten million houses by providing them with accessible electricity units, amounting to three hundred each month.
The role of stakeholders
The government’s basic role is majorly centered on policy creation and regulation. This is done by setting up systems that improve renewable energy investment and keep the grid stable. Large investments are also made in transmission networks and smart grids to improve electricity distribution efficiency.
The private sector is a powerful force behind innovations and investments in renewable energy projects. Averting from dirty forms of energy, fostering partnerships, and clean technology pioneers within industries are some examples of what companies engage in. Therefore, it is essential to note that their contribution is imperative for the economy’s growth and job provision within this renewable energy sector.
The public has a role in promoting energy conservation and demand-side responses. By adopting various practices that lead to efficient power use, they can greatly influence electricity demand, thereby lowering their carbon footprint.
Community engagement, including awareness programs, is vital in teaching communities about the clean benefits of renewable energy and its importance in conserving energy. These programs empower local actors to save power, changing behavior toward sustainable energies.
Conclusion
As India continues its journey towards a more sustainable energy future, integrating advanced technologies, robust regulatory frameworks, and inclusive community participation will be vital to achieving energy security, economic prosperity, and environmental stewardship.
By leveraging its strengths and proactively addressing challenges, India is poised to emerge as a global leader in clean energy solutions, setting a precedent for other nations to follow in the pursuit of a cleaner and brighter tomorrow.
DISCLAIMER: This article is not meant to be giving financial advice. Please seek a registered financial advisor for any investments.
- Make in India 2.0: How Manufacturing Is Reshaping Market Sentiment - December 13, 2025
- Real Estate Boom : Why Tier-2 Cities Are Attracting Big Investors - December 12, 2025
- India’s GDP Surge 2025: What the New Growth Numbers Mean for Markets - December 9, 2025





